Blog
TMS Depression Treatment: The Non-invasive Solution for Treatment-Resistant Depression
- March 29, 2023
-
NeuroMod Health

When it comes to mental health, depression is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While traditional treatment methods such as medication and therapy have been effective for many individuals, some may find limited relief or experience intolerable side effects.
For those struggling with treatment-resistant depression, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) offers a promising alternative. In this article, we will explore TMS depression treatment, its efficacy in targeting specific areas of the brain, and its potential as a noninvasive option for individuals seeking relief from depression symptoms.
Recent Posts

Does TMS Hurt? Common Myths About the Procedure


What Teens Can Expect During Their First TMS Session

Contents
- What is TMS depression treatment?
- When did TMS treatment get FDA approved?
- What conditions can be treated with TMS treatment?
- What are the key advantages of TMS depression treatment over Electroconvulsive Therapy.
- What does the TMS depression treatment process consist of?
- Why choose AscendTMS for TMS depression treatment?
What is TMS depression treatment?
TMS depression treatment is a noninvasive procedure that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific areas of the brain. It is primarily targeted at the prefrontal cortex, a region associated with mood regulation. By delivering magnetic stimulation to this area, TMS aims to modulate neuronal activity and restore the balance of brain chemicals involved in depression.
TMS is an FDA-approved therapy for major depressive disorder and treatment-resistant depression, offering a safe and effective alternative for individuals seeking relief from depression symptoms. It is well-tolerated, does not require anesthesia, and has minimal side effects, making it an attractive option for many patients.
When did TMS treatment get FDA approved?
The development of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) as a treatment for depression stems from the exploration of brain stimulation therapies. In the early 1980s, Dr. Anthony Barker pioneered TMS, initially using it as a tool to study brain function. As researchers recognized its therapeutic potential, TMS shifted towards becoming a treatment modality.
Extensive clinical research in the late 1990s demonstrated its efficacy in depression treatment. In 2008, the FDA approved TMS for major depressive disorder, offering hope to those with treatment-resistant depression. TMS is a noninvasive and well-tolerated intervention, targeting specific brain areas. As our understanding of the brain evolves, TMS continues to advance, providing an alternative for individuals seeking relief from depression symptoms and driving further innovation in brain stimulation therapies.
What conditions can be treated with TMS treatment?
While TMS is primarily known for its effectiveness in treating depression, its applications extend beyond this disorder. Research has shown promising results in using TMS to address other mental health conditions, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and anxiety disorders.
The ability to target specific areas of the brain using magnetic stimulation opens up possibilities for a broader range of treatment options in the field of mental health.
TMS therapy can also be used in conjunction with other treatment modalities, such as medication and therapy. Some individuals may find that TMS enhances the effectiveness of their current treatment plan, leading to better outcomes.
It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable treatment approach for each individual’s unique needs.
What are the key advantages of TMS depression treatment over Electroconvulsive Therapy.
TMS treatment is a noninvasive procedure that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate specific areas of the brain associated with depression, while electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) involves inducing controlled seizures through electrical currents to treat severe depression
TMS is a more appealing option for individuals seeking depression treatment as the table of advantages below can attest to.
TMS vs ECT
Noninvasive Procedure
| TMS is a noninvasive treatment that does not require anesthesia or cause memory loss, unlike ECT. This aspect makes it more appealing to individuals who may be hesitant about undergoing invasive procedures.
|
Absence of Anesthesia
| TMS does not require general anesthesia, eliminating the potential risks and side effects associated with anesthesia administration.
|
Minimal Side Effects
| TMS is generally well-tolerated and has fewer side effects compared to ECT. Common side effects of TMS include mild scalp discomfort or headache, which typically subside shortly after the session.
Patients can drive themselves to the practice and back home after a therapy session. |
Preserved Cognitive Function
| Unlike ECT, which can cause temporary memory loss and confusion, TMS does not adversely affect cognitive function. Patients can continue their daily activities immediately after the session without experiencing cognitive impairment.
|
Outpatient Treatment
| TMS therapy is typically performed in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to return home after each session. This convenience reduces the need for hospitalization or overnight stays, resulting in minimal disruption to the individual’s daily life.
|
Precise Targeting of Brain Regions
| TMS allows for precise targeting of specific areas of the brain, such as the prefrontal cortex, which is implicated in depression. This targeted stimulation helps modulate brain activity and restore the balance of chemicals involved in mood regulation.
|
Gradual and Controlled Stimulation
| TMS delivers magnetic pulses in a gradual and controlled manner, making it a safer option compared to the induced seizures of ECT. The ability to fine-tune the stimulation parameters allows for individualized treatment tailored to each patient’s needs.
|
Lower Treatment Risks
| TMS has a lower risk profile compared to ECT, making it suitable for individuals who may be at higher risk or have medical conditions that preclude them from undergoing ECT. TMS is generally considered a safer alternative for patients with cardiac conditions or other health concerns.
|
Improved Treatment Acceptability
| The noninvasive nature and minimal side effects of TMS make it a more acceptable treatment option for many individuals who may be reluctant to pursue ECT due to concerns about anesthesia, memory loss, or other associated risks.
|
Potential for Combined Therapies
| TMS can be used in combination with other treatment approaches, such as medication and therapy. It can enhance the efficacy of existing treatments, providing a comprehensive and holistic approach to managing depression symptoms.
|
What does the TMS depression treatment process consist of?
The process of receiving TMS treatment typically involves several steps. Firstly, a thorough evaluation is conducted by a qualified healthcare professional to determine if TMS is a suitable treatment option for the individual.
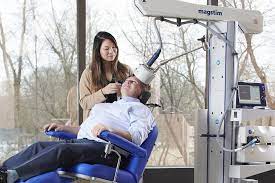
Once TMS is deemed appropriate, the patient is comfortably seated in a treatment chair. A specialized device, known as a TMS coil, is placed on the patient’s head, specifically targeting the prefrontal cortex or other identified areas of the brain.
During the session, the TMS device delivers magnetic pulses to the targeted brain regions. These pulses create small electrical currents that stimulate the nerve cells in that area. The patient may feel tapping or clicking sensations on the scalp during the procedure, but the treatment is generally painless.
The duration of a TMS session can vary, typically lasting between 19 and 37 minutes. The frequency and total number of sessions required depend on the individual’s treatment plan, which is determined by the healthcare professional. TMS therapy usually involves daily sessions, five days a week, over several weeks.
Throughout the treatment course, patients can resume their daily activities immediately after each session, as there is no recovery time or anesthesia involved. TMS is performed on an outpatient basis, allowing individuals to return home or continue with their regular routine after the treatment session.
It’s important to note that TMS treatment is generally covered by health insurance, although coverage specifics may vary depending on the provider and policy. Regular follow-up appointments and evaluations are scheduled to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
Why choose AscendTMS for TMS depression treatment?
With a focus on individualized treatment plans, NeuroMod Health ensures that each patient receives tailored care to address their unique needs and goals. The clinic’s commitment to patient comfort, safety, and satisfaction is evident throughout the treatment process.
Additionally, NeuroMod Health is well-equipped with state-of-the-art TMS technology and maintains a supportive and compassionate environment that fosters healing and recovery. If you would like to learn more about TMS depression treatment and if you would be a suitable candidate for TMS therapy, contact us and one of our passionate team members will get back to you as soon as possible.